Non-Unique Emails is currently in Early Access. To learn more about Auth0 releases, review Product Release Stages.
Considerations
Review the following to ensure Non-Unique Emails is the right fit for your use case.Primary identifier requirements
Email cannot be used as the primary identifier when using Non-Unique Emails. You must configure another attribute as the primary identifier, which will be used for authentication, password resets, and account management. For more information about identifiers and attributes, read Flexible Identifiers.Password resets
End users must provide their username, phone number, or whichever attribute their administrator configured as the primary attribute when resetting their password. Auth0 uses that primary identifier to locate and reset the account associated with a shared email address.Irreversible settings
Once the email attribute is set to non-unique on a connection, it cannot be changed back to unique. In addition, only new database connections can be created with non-unique email support; you cannot change an existing connection, and you must update your app to use the primary identifier you choose.Flexible identifiers
Flexible Identifiers must be enabled on the database connection to use Non-Unique Emails and they cannot be disabled after the connection is created. When you enable Non-Unique Emails with the , Flexible Identifiers are configured for you automatically.API behavior changes
GET /api/v2/users-by-email returns all users that share the same email address.
DELETE /api/v2/connections/{id}/users is not compatible with non-unique email connections.
POST /dbconnections/change_password does not work with Non-Unique Email connections because it requires a unique email address to find the user account. Users must use flows that leverage the primary identifier to reset their passwords.
Enable Non-Unique Emails in the Auth0 Dashboard
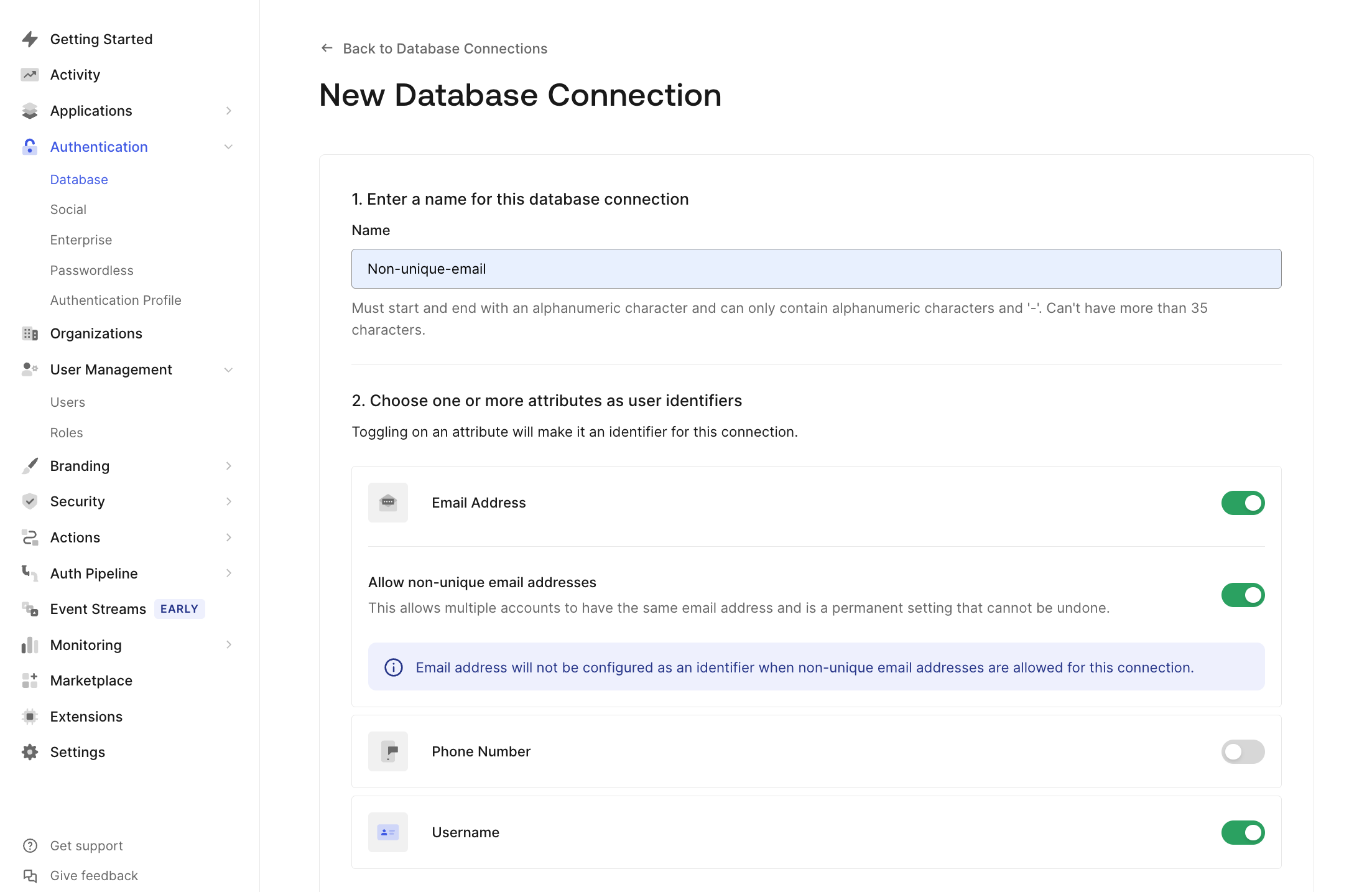
- Go to Authentication > Database andcreate a new connection.
- Navigate to the Choose one or more attributes as user identifiers section and toggle Email Address to On, then enable the Allow non-unique email addresses toggle that appears.
- Pick either username or phone number to toggle On as well to serve as a primary identifier for login and password reset flows.
- After confirming that email will not be used as an identifier, choose Create to save the Connection.
Enable Non-Unique Emails via the Management API
Use thePOST /api/v2/connections endpoint in the Management API to create a database connection that supports Non-Unique Emails.
When creating the connection:
- Set unique: false in the
options.attributes.emailobject to allow multiple accounts with the same email address. Set identifier.active: false to ensure that the email cannot act as the primary identifier when it’s not unique. - Choose another attribute as the primary identifier and set identifier.active: true for the attribute you chose.
Example request
Below is an example of a request body to create a database connection that uses a username as the primary identifier and supports non-unique emails:Shared Email Risk Disclaimer
While the Non-Unique Emails feature includes safeguards, such as disallowing email as a primary identifier and requiring password resets to be performed using a username or phone number**,** there is still inherent risk when multiple user accounts share the same email address. For example:- All email communications (e.g., password reset links, notifications) will be delivered to the same inbox, regardless of which user initiated the action.
- This could lead to confusion for users or unintended access to email-based links if the inbox is shared.
- Shared email scenarios are appropriate for your use case.
- End-users are informed and trained accordingly.
- Your application design accounts for potential overlaps in email-based workflows.

